Ancient Egyptian Mummies still have a strange appeal that catches our attention. These well-preserved bodies, carefully wrapped in linen wraps and buried with complex rites, show ancient Egyptian history and culture. In this blog post, we’ll go on an adventure to learn more about the mysterious world of Egyptian mummies. We’ll also talk about what they meant to ancient Egyptians and why we’re talking about them today.
Ancient Egyptian burial customs, which go back more than 5,000 years, led to the making of mummies. To mummify a body, the innards had to be carefully removed, the body had to be preserved by embalmed, and then it had to be wrapped in layers of linen wraps. This careful process was meant to keep the dead from decaying on their way to the heavens so that their bodies would stay the same for all time.
Mummification was not just something that only the rich or the pharaohs did; it was a common practice in all parts of ancient Egyptian society. Everyone, from pharaohs to commoners, thought it was important for the soul’s trip to the future to be saved after death. Ancient Egypt’s views and social norms changed over time, as did the ceremonies and methods used for mummification.
As we learn more about old Egyptian mummies, this blog post aims to give readers a complete picture of these exciting objects. We’ll talk about the background and meaning of mummification in Egyptian society and the methods and rituals used in the process. We’ll also talk about the beliefs and practices related to the future.
Through this research, we hope to learn more about ancient Egyptian mummies’ cultural, political, and spiritual meanings. This will give us a better understanding of the fascinating culture that left these unique relics behind. So, join us on this exciting trip into old Egypt and its famous mummies.
Origins and History of Mummification in Ancient Egypt
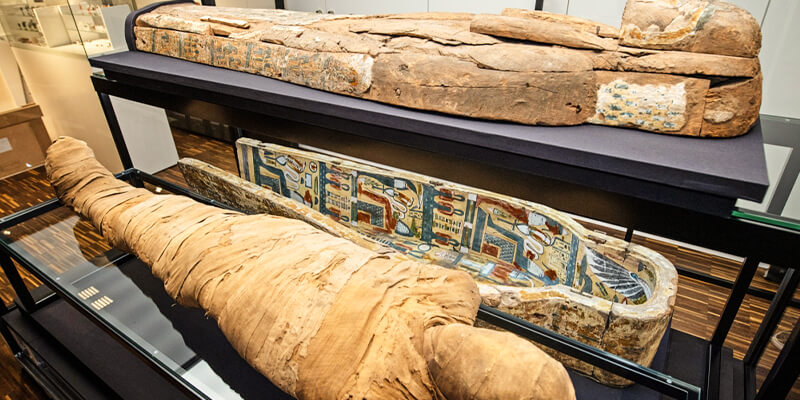

A. Initial experiments and the creation of methods for mummification:
The old and mysterious of ancient Egypt came up with mummification as a way to keep the bodies of the dead for all time. The practice of mummification has been around for more than 4,500 years. It began in Egypt during the Early Dynastic Period. But it didn’t happen all at once. Instead, it was a slow, complicated process that grew over time.
In the beginning, mummification was a rough and untested process. In the first efforts, the bodies were just buried in the dry sands of a desert, which led to some natural preservation. As the ancient Egyptians watched this natural preservation, they saw that there was a way to keep the bodies of their loved ones even longer.
These early tests created a new, more organized way to mummify bodies. The internal parts had to be removed and treated with natron, a type of salt, to keep them from becoming rancid. It was also wrapped and treated with glue and tar to keep the body from going wrong. Over time, mummification methods improved, and traditions were made to ensure they worked.
B. Connection to religious beliefs and the afterlife:
Mummification in ancient Egypt was not merely a physical preservation method but was deeply intertwined with their religious beliefs and the concept of the afterlife. Ancient Egyptians believed that for the soul, or ka, to live on after death, it needed a body that was well taken care of. People thought that mummies gave the ka a body to live in after they died and left this world.
People thought that keeping the body alive was an essential part of going to the future. People believed the body should look like it did when it was healthy so that the ka could know and connect with it. The preserved body was a home for the soul, so it could keep its identity and enjoy a future full of pleasures that would never end.
Very skilled embalmers performed mummification practices to ensure the dead went to the next world without any problems. In ancient Egypt, these embalmers were very important from a religious point of view because they knew how to prepare the dead for their trip to the afterlife.
C. Evolution of mummification practices over time:
As ancient Egypt’s culture grew, so did the art of preserving dead bodies. Over the ages, the process changed a lot as new skills and routines were added. Methods for mummifying the dead improved based on the person’s social standing and wealth.
During the Middle Kingdom, mummification became more accessible for more people, and the ways to do it improved. The internal parts were no longer taken out entirely. Instead, they were left in place and kept alive. Still, natron was used, but it was done more formally and successfully, improving preservation overall.
When the New Kingdom came, mummification hit its highest point. The embalmers were experts at their job. They made detailed masks and elaborate graves and used bright colors to make the mummies look more beautiful. It became a sign of wealth, and the more complicated the process was, the richer the person was.
The fact that ancient Egyptians mummified their dead showed how deeply they believed in the future and how important it was to keep the body alive. This unique way of burying the dead continues to interest people worldwide. It tells us a lot about the ancient Egyptians and their strong belief in the soul’s immortality.
The Mummification Process
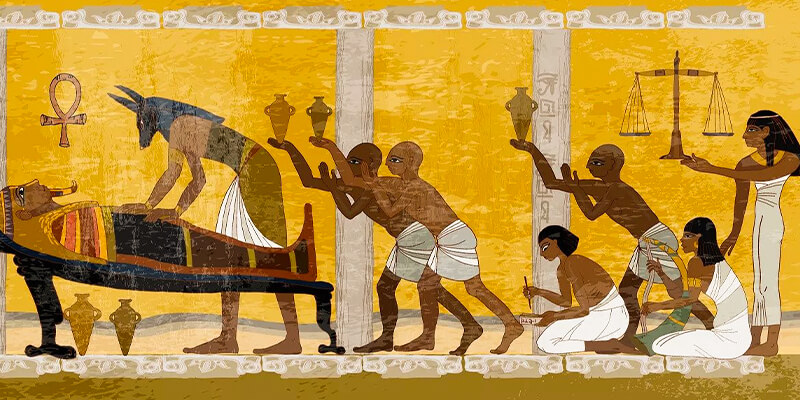

A. A step-by-step guide to the process of mummification:
In ancient Egypt, mummification was a complicated and careful process that was meant to keep the body of the dead for all time. It was essential to their faith practices and ideas about the future. There were several steps to the process, each important for keeping the body in good shape.
First, the body was taken to the per nefer, the embalmers’ workplace. Here, water from the Nile was used to wash and clean the body carefully. Once the body was clean, the parts were taken out, except for the heart, which was considered necessary for the journey to the future.
Next, a natural salt called natron was used to treat the body. A lot of natron was packed around the body, which kept the body from getting wet. This process aims to dry the body and stop it from breaking down.
After about 40 days, when the body was dehydrated, the embalmers started to wrap it. Soaked in resin, strips of linen were carefully wrapped around the body, ensuring every part was covered. Amulets and charms were also between the layers to protect the dead person.
Lastly, once the mummy was all wrapped up, it was put inside several tombs, each with beautiful artwork. These tombs added an extra layer of defense and showed the rank and wealth of the dead person.
B. The role of the embalmers and priests:
In ancient Egypt, trained embalmers knowledgeable about body preservation performed the mummification process. But the priests’ part was just as vital because they directed and led different religious practices during the process.
The embalmers, who were considered to be skilled craftspeople, carefully performed the mummification process. Their knowledge of anatomy was necessary for taking out and keeping the organs in good shape. They were in charge of the physical parts of mummification and had to follow complicated religious and cultural rules.
On the other hand, the priests were critical of the spiritual side of mummification. They prayed and practiced to ensure the dead would have a good time in the afterlife. Priests also did a rite called “Opening of the Mouth,” which people thought would allow the mummy to see, breathe, eat, and talk in the future.
Priests and embalmers worked closely, using their skills and knowledge to ensure the mummification process was done with the most fantastic accuracy and respect for religious rules.
C. The tools and items used to preserve the body:
The ancient Egyptians used many tools and materials during the mummification process. These things were chosen carefully to achieve the goal of keeping the body for all time.
The “adze,” shaped like a hook, was one of the main tools embalmers used. It helped them take the brain out through the nose. Another important tool was the “hooked knife,” which allowed the embalmers carefully remove the body’s innards.
Regarding the things used, natron was a vital part of preserving. It was a salt found naturally in desert areas and an essential dehydrating agent. Natron was used to completely dry out the body, which stopped it from breaking down.
Also, cloth strips soaked in resin were used to wrap the body. The glue worked as a preserve, keeping the body from breaking down and preventing it from rotting. Fine linen and other high-quality and expensive fabrics were often used to wrap the body. This added a sense of respect and honor to the process.
Overall, the mummification process needed specific tools, carefully chosen materials, and the skills and knowledge of embalmers and priests to ensure that the dead were kept safe and ready for their trip to the future.
Beliefs and Rituals Surrounding Ancient Egyptian Mummies
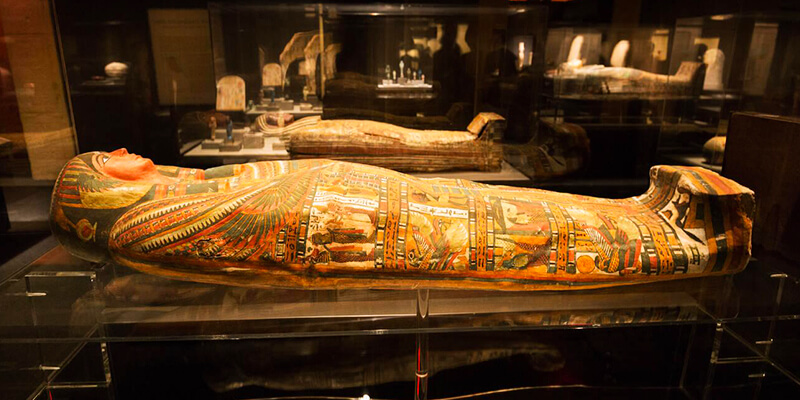

A. The significance of the afterlife in Ancient Egypt
Ancient Egyptians had strong views about the future. They thought of it as an essential part of their lives on Earth. They felt that death was a step toward a new life that would last forever. The mummification process kept their bodies in good shape and ensured they were ready for the trip to the future.
Ancient Egyptians thought that when a person died, their soul, called “ka,” went to the Hall of Ma’at, where the gods would judge them. They thought the dead person’s heart would be compared to the feather of Ma’at, which stood for truth and justice. If the person’s heart was clean and they had followed the rules of Ma’at during their life, they would be allowed to go to the future. So, mummification was essential to keep the body alive because it was a way for the soul to continue its trip.
B. The role of mummification in making sure a person’s trip to the future goes well
Ancient Egyptian ideas and practices about death and the future were based on mummification. To mummify a body, the parts inside, such as the brain, lungs, intestines, and liver, had to be carefully removed and put in canopic jars to keep them from rancid. The body was then washed and treated with natron, a natural salt, for about 40 days to get rid of extra water and stop the body from breaking down. The dead person’s body was then covered in cloth wraps, sometimes decorated with amulets and charms to protect them on their way to the heavens.
People thought mummifying the body would keep it whole so the dead could know and meet up with their ka. Ancient Egyptians believed that if they kept their bodies, they could live forever, keep their memories, and live the same way they did while they were alive.
C. The funeral rites and traditions that go along with mummification
During the process of mummification, different funeral rites and events took place. These practices aimed to ensure that the body would stay alive and that the person could go to the future. The innards out of the body by the embalmers called “sewekhemsaf.” People thought these people were very skilled and vital to society because they were essential to the dead’s journey to the afterlife.
After the body was mummified, different ceremonies were held. One of these was the Opening of the Mouth ceremony, in which a priest would magically reopen the mouth of the dead person so they could eat and drink in the future. Food, drink, and personal items were offered in the tombs so that the deceased would have what they needed in the end. The ancient Egyptians thought these gifts would keep the soul alive and ensure the dead person would continue to live and be happy forever.
In the end, the ancient Egyptians gave the future a lot of importance and had a lot of complicated beliefs, rites, and ceremonies about mummification. They thought that mummification kept the body alive so it could go to the heavens and live forever. These ideas and practices tell us a lot about how the ancient Egyptians saw the world and how much they respected life, death, and the afterlife.
Types of Ancient Egyptian Mummies
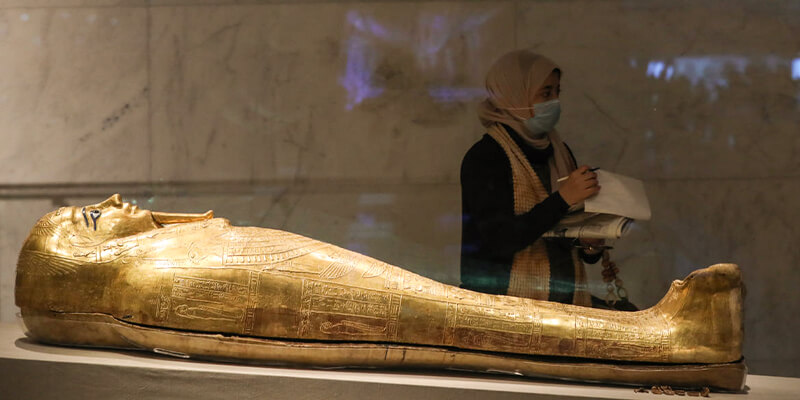

A. Royal mummies and their unique preservation methods
In the fascinating world of ancient Egypt, mummification is often linked to the gods, as shown by the way royal mummies were kept. These unique bodies were made with unmatched attention to detail and were kept alive in ways that made them stand out. The process of mummifying a Pharaoh involved complex customs and careful steps that made sure the king would live forever after death. The whole thing took an agonizingly long to finish, sometimes taking up to 70 days.
Removing internal parts was a notable way royal mummies were kept in good shape. People thought these parts, called “vital organs,” could stop mummification. Instead of throwing them away, they were carefully kept in canopic jars. Then, these jars were put in the tomb with the mummy to show that they would help the king in the future.
The careful process of wrapping the Pharaoh’s body in layers of cloth wraps was another unique part of royal mummification. Non-royal mummies were often only lightly dressed, but royal mummies wore beautiful linen masks to show they were gods. These masks had detailed designs and were sometimes made of gold or expensive stones. The fact that these masks were made with so much care showed that the Pharaoh was a king and close to the gods.
B. Non-royal mummies and differences in mummification techniques
Even though royal mummies are the most well-known and respected, the ancient Egyptians also buried people who were not royalty, though they did so in different ways and for various reasons. People who weren’t royalty often used a simpler version of the mummification process that worked with the tools and resources they had.
People who weren’t royalty didn’t have their parts taken out as royal mummies did. Instead, the body openings were filled with herbs and chemicals to stop decay. Even though this method wasn’t as complicated as the royal method, it still made it possible to keep things for a long time.
The way they are wrapped is another difference. Most non-royal mummies had fewer layers of linen wraps and were wrapped more freely. The goal was to keep the person alive, not to make fancy funeral displays. But it’s important to remember that even non-royal mummies were treated with respect and care, which shows how vital the afterlife was to ancient Egyptians.
C. Animal mummies and their purpose in ancient Egyptian culture
Animals were also preserved in the old Egyptian civilization, which led to the creation of exciting animal skeletons. Animal mummification was a big part of Egyptian religious practices and beliefs and served many uses.
One common reason for mummifying animals was to give them to the gods as gifts. Egyptians thought that when preserved animals were put in holy places or shrines, they could help people communicate with the gods. Cats, bulls, birds, crocodiles, and even scarab bugs were all chosen because they were linked to different gods.
Also, in the afterlife, animal mummies accompanied their human peers. People thought that the souls of these animals would help the dead on their way to the divine world. Because some animals, like the strong lion and the graceful falcon, were seen as symbols, mummifying them let the dead use the traits and skills associated with these animals.
Ancient Egyptians’ complex beliefs, deep knowledge of life and death, and unwavering dedication to the holy were shown by how they preserved royal, non-royal, and animal bodies. These mummies tell us about a culture that respected the future and made terrific connections between humans and gods that still amaze us today.
Discoveries and Study of Ancient Egyptian Mummies
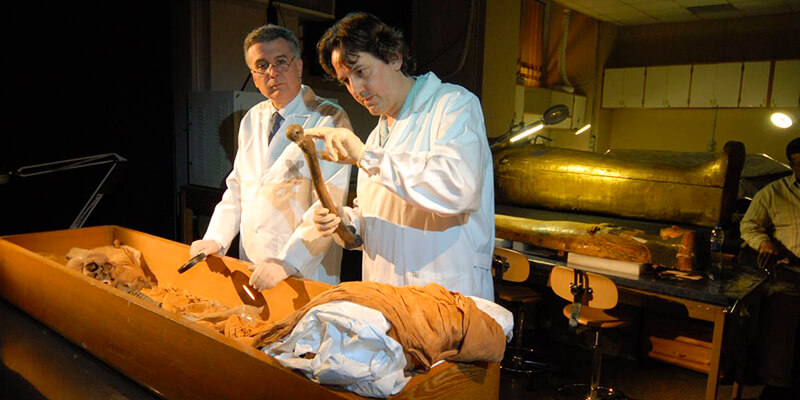
A. Famous archaeological finds of intact mummies:
Finding whole bodies is one of the most exciting things about ancient Egypt. The world has been fascinated by these fantastic historical finds, which have taught us a lot about how the Egyptians lived. Famous mummies like Tutankhamun, Ramses II, and Hatshepsut have been carefully found, giving us a look at how the ancient Egyptians died and what they thought about the future.
When Tutankhamun’s tomb was found in 1922, it changed everything in Egyptology. The young pharaoh’s mummy was beautifully kept in several stacked vaults. This showed how complicated the burial process was and how much the ancient Egyptians cared for their dead. It was a rare chance to glimpse the pharaohs’ world and the grandeur that went along with it.
B. Modern scientific techniques used to study mummies:
Modern scientific progress has allowed us to study old Egyptian bodies in a way that doesn’t hurt them. Non-invasive methods like computed tomography (CT) scanning, X-ray images, and DNA analysis have become very helpful in figuring out what these preserved bodies were and how they were kept.
CT scanning is beneficial for getting detailed pictures of frozen bodies without damaging their fragile structures. With this technology, we can “virtually unwrap” the mummies to find secret amulets, jewelry, or even the person’s health problems.
Also, taking DNA from old Egyptian bodies and analyzing it has given us a lot of information about their family connections, diseases they might have had, and where they came from. These scientific breakthroughs help us learn more about how the ancient Egyptians lived and show us more about their genetic past.
C. Insights gained from studying ancient Egyptian mummies:
Researchers have learned much about ancient Egyptian society by looking at their mummies. They have known about their religious views, medical knowledge, and social organization, among other things. We have learned much about the practices and beliefs surrounding death and the future by examining the tombs’ mummies, bones, and other items.
For example, the complex amulets and charms put on mummies were meant to protect and help the dead on their way to the future. The ancient Egyptians’ advanced knowledge of human anatomy and burial methods was shown by how well they could preserve the body during the complicated mummification process.
The social structure of ancient Egypt has also been shown by studying bodies and the things they were buried with. The wealth and social status of the dead could be seen in how much money was spent on the funeral, the quality of the tombs, and the other funeral items. With this information, we can put together the social order of ancient Egypt and learn more about how people of different groups lived.
Ultimately, the discovery and study of ancient Egyptian mummies have fascinated people worldwide and taught us a lot about one of the most exciting societies in human history. We continue to learn essential things about their views, habits, and way of life from these historical finds and modern science studies.
Famous Ancient Egyptian Mummies
A. Tutankhamun and the discovery of his tomb
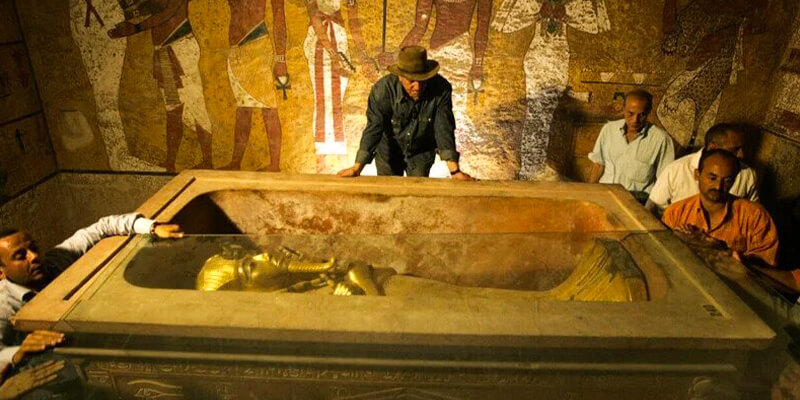

The mummy of Tutankhamun, also known as King Tut, is one of the most well-known and interesting ones from ancient Egypt. Tutankhamun became king of Egypt when he was only nine years old. He was in charge for a short time in the 14th century BC. Howard Carter, a British researcher, found Tutankhamun’s tomb in 1922, which makes him and his mummy so interesting. The discovery of the complete tomb full of riches, including Tutankhamun’s ideally kept-mummy, was a significant turning point in Egyptology.
The tomb contained many layers of beautifully made gold objects, funeral masks, and valuable jewels. These items were gifts for the pharaoh’s death, which shows his rule’s greatness. The fact that Tutankhamun’s mummy was found in a beautiful coffin with beautiful gold shows how vital the young ruler was. Due to his brief life and the fact that he belonged to a royal family with numerous cousins, Tutankhamun had several health issues.
B. Queen Hatshepsut and her mummy’s intriguing history
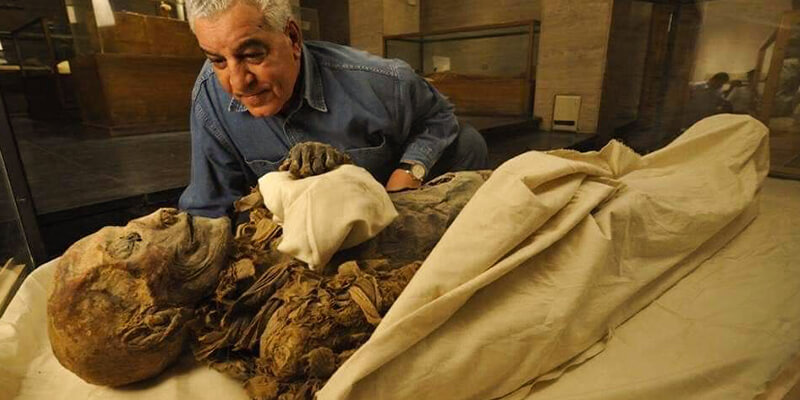

Queen Hatshepsut was one of ancient Egypt’s most potent and famous pharaohs. She continues to fascinate scholars and fans all over the world. Hatshepsut became ruler of Egypt in the 15th century BC. She was a strong and successful leader who brought peace and wealth to the country. Hatshepsut was buried in the Valley of the Kings after she died. Like many other mummies, hers was mainly left alone for hundreds of years.
But it wasn’t until 1903 that the famous researcher Howard Carter found the tomb of Sitre In, who was thought to have been Hatshepsut’s wet nurse. The tomb also held pieces of Hatshepsut’s mummy. This finding led to more guesses about where Hatshepsut’s mummy might be.
Only in 2007 did a group of Egyptian researchers say they had found her bones. The mummy, which at first was thought to be of a male monarch, was found to be that of Queen Hatshepsut after years of careful study. DNA research and unique physical traits found in the tomb of Hatshepsut’s royal builder were used to figure out who the person was. This fantastic find throws light on the mysterious ruler’s life and gives us a look at the world of ancient Egypt.
C. Ramses II, the “Great Ancestor,” and his well-preserved mummy
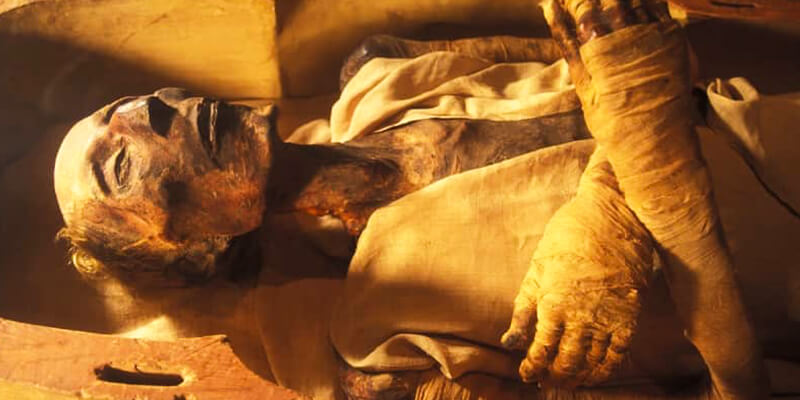

Ramses II was one of Egypt’s most powerful pharaohs. He is often called the “Great Ancestor” because his family tree goes a long way. Ramses II was one of Egypt’s most respected kings. During his reign in the 13th century BC, he won war victories, built massive structures, and made peace with other countries. The fact that Ramses II’s mummy is so well-kept tells us a lot about this famous pharaoh’s life and memory.
Ramses II’s body was found in the royal cache at Deir el-Bahari in 1881. This is where the mummies of several pharaohs were hidden to keep them safe from grave thieves. Even though Ramses II lived over 3,000 years ago, his mummy is incredibly well preserved. It shows detailed details of his face and even some red hair. Ancient Egyptian burial methods and the safe surroundings of the hidden tomb may have helped the mummy stay in good shape.
Today, Ramses II’s mummy is in the Egyptian Museum, where people can see how beautiful the king was, who left a lasting mark on ancient Egyptian history. Ramses II’s obelisks, temples, and statues still stand all over Egypt, and his well-preserved mummy is a reminder of his great rule.
The Legacy of Ancient Egyptian Mummies

A. The influence of mummification on later civilizations and cultures
Ancient Egypt’s practice of mummification has left a lasting mark on later cultures and civilizations. You could say that old Egyptian mummies have significantly impacted our thoughts on death and the future. As the Egyptians believed that keeping the body alive was necessary for the soul’s journey through eternity, mummification became an essential part of their religion and spiritual views.
This old Egyptian custom interested people from other countries and affected how they buried their dead. For example, the most influential people in the Roman kingdom were embalmed, similarly to how the Egyptians did it. This shows how much people admired this complicated way of preserving bodies. During the Middle Ages, Europeans used similar methods to protect the bodies of kings and other important people. Ancient Egyptians used complex rites and practices for preserving bodies that were used by later societies as models. This shows how vital mummification was to later cultures.
B. The impact on modern understanding of ancient Egypt and its people
Ancient Egyptian mummies have given modern scientists, archeologists, and historians a lot of information about ancient Egypt and its people that they could not have gotten any other way. Historians have learned much about old people’s daily lives, religious views, and even their health and looks by looking at mummies.
Scientists have figured out how the ancient Egyptians got sick and what diseases they had by looking at the bodies found in tombs. When CT scans were done on mummies, they showed signs of conditions like hunger, tooth problems, and even surgeries during their time. Researchers have also learned much about ancient Egyptian medicine and burial methods from the parts still in the mummies’ bodies.
C. The public’s preoccupation with old Egyptian corpses
Ancient Egyptian mummies have captivated popular culture for centuries. From books to movies, they have become a sign of wonder, intrigue, and the unknown that will last for a long time. The interest in mummies can be traced back to the early 1800s when mummies were brought to Europe and displayed in shows that wowed people with their strange appearance.
In many books and stories, mummies are often presented as old beings with magical powers which can be brought back to life to cause trouble in the modern world. The lasting success of Bram Stoker’s “The Jewel of the Seven Stars,” in which an Egyptian mummy is brought back to life, shows how much people like mummies. The story’s creepy and fantastical plot keeps people reading.
Since the beginning of the 20th century, mummies have been a repeating theme in movies. Iconic movies like “The Mummy” series have left a lasting mark on pop culture. The mummies in these movies are often shown as evil and cursed. They bring ancient Egypt to life on the big screen and cement their place in popular culture.
Ultimately, mummies from ancient Egypt have significantly affected many parts of our society. Mummies have substantially impacted how we think about the ancient Egyptians today. For example, they changed how other cultures buried their dead and gave us essential information about their lives. Also, the fact that they are still talked about in pop culture shows how mysterious and exciting these old artifacts are.
In conclusion
it’s impossible to say enough about how vital Ancient Egyptian mummies are. These bodies that have been kept in reasonable condition give us essential information about the beliefs, customs, and society of one of the world’s most significant societies. The Egyptians were very careful with every step of the mummification process, which shows how much they cared about the future.
Ancient Egyptian bodies have left behind much more than their historical value. People have been fascinated by them for a long time, and they have inspired many art, writing, and movies. From the beautiful sarcophagi with intricate hieroglyphics to the cursed tomb of Tutankhamun, these mummies have become powerful images of Egypt’s glorious past.
Mummies are essential to our culture, but they have also helped us learn a lot about old science and the human body. Because the Egyptians took good care of their artifacts, experts today can look at their health, food, and diseases to learn more about how medicine was done in a long-ago time.
If you are interested in Ancient Egypt because of its beauty, I encourage you to learn more about it by studying mummies, which can tell you a lot about its long and fascinating past. You can see these amazingly well-preserved bodies in a museum or take a video walk of the famous Valley of the Kings. Read academic articles and books, or watch films about mummification practices and the beliefs the Egyptians used to guide them on their way to the future.
By learning about the past and impact of Ancient Egyptian mummies, we can better understand what this fantastic society was able to do. These mummies are not just macabre oddities but windows into a world that once thrived, where art, faith, and science met in unique ways. So, let’s take advantage of the chance to learn from history and get lost in the charm of Ancient Egypt’s mummies.
Are you yearning for an adventure of a lifetime? Look no further than the captivating land of Egypt, where ancient wonders and vibrant culture await. With many Egypt vacation packages, day tours, and Nile cruises to choose from, your journey through this historical treasure trove is bound to be unforgettable. Immerse yourself in the mystique of the pyramids of Giza, marvel at the grandeur of the temples of Luxor, and embark on a once-in-a-lifetime cruise along the majestic Nile River. From the bustling streets of Cairo to the serene beauty of Aswan, Egypt offers a myriad of experiences for every traveler. Whether you crave the thrill of exploring the ancient tombs of the Valley of the Kings or the tranquility of sailing on a traditional felucca, Egypt’s diverse landscapes and rich history will leave you awe-inspired. Don’t miss out on the opportunity to unravel the secrets of the Pharaohs and create lasting memories on your Egypt vacation. Book your Egypt vacation package, day tour, or Egypt Nile cruise today, and let the magic of this enchanting destination unfold before your eyes.

